Biogas cogeneration
- Home
- Biogas cogeneration
Renewable electrical and thermal energy from organic residues.
Biogas is a natural fuel that is obtained through anaerobic digestion, i.e. bacterial fermentation that takes place in the absence of oxygen of organic residues from plant or animal residues.
About 50-70% of the biogas produced is made up of methane and the remainder of carbon dioxide and other minor components. If adequately processed, it is able to power the internal combustion engine of a cogeneration plant and to produce totally renewable electricity and thermal energy.
Products
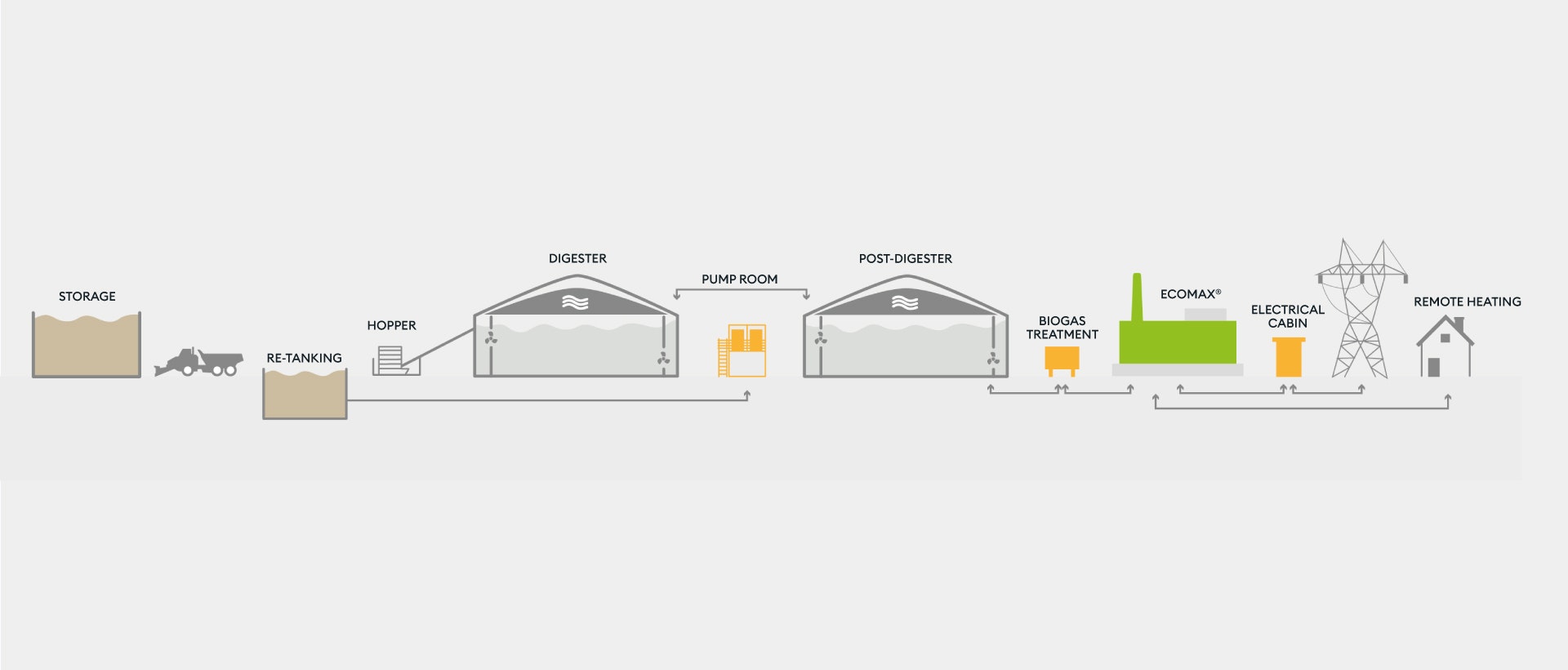
How a biogas plant works
A biogas plant consists mainly of two parts: the anaerobic digestion part, where the actual production of biogas takes place (consisting of one or more digestors) and the transformation of biogas into energy part, i.e. the cogeneration plant.
Biogas can be produced starting from different raw materials, such as livestock effluents, sludge from wastewater treatment plants, Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste (OFMSW), agro-industrial waste and crop residues. The energy yield, in terms of biogas produced and therefore of electrical and thermal energy generated, varies according to the characteristics of the raw material chosen.
Digestors play a key role in the initial phase of the biogas production process, but the energy efficiency and overall economic performance of the plant depend on the quality and reliability of the technological solutions that make up the cogeneration group.
Energy produced
Electric power
to be sold to the network
Thermal energy
for production of:
• hot water
• steam
• cold water
Technologies and operating process of a biogas CHP plant
Sectors of applications
Agriculture
Landfills/OFMSW
Agro-industrial waste
Wastewater treatment